New Breakthrough in Declarative Graph Benchmarking: GraphScope Flex Shatters LDBC SNB Interactive Benchmark World Record
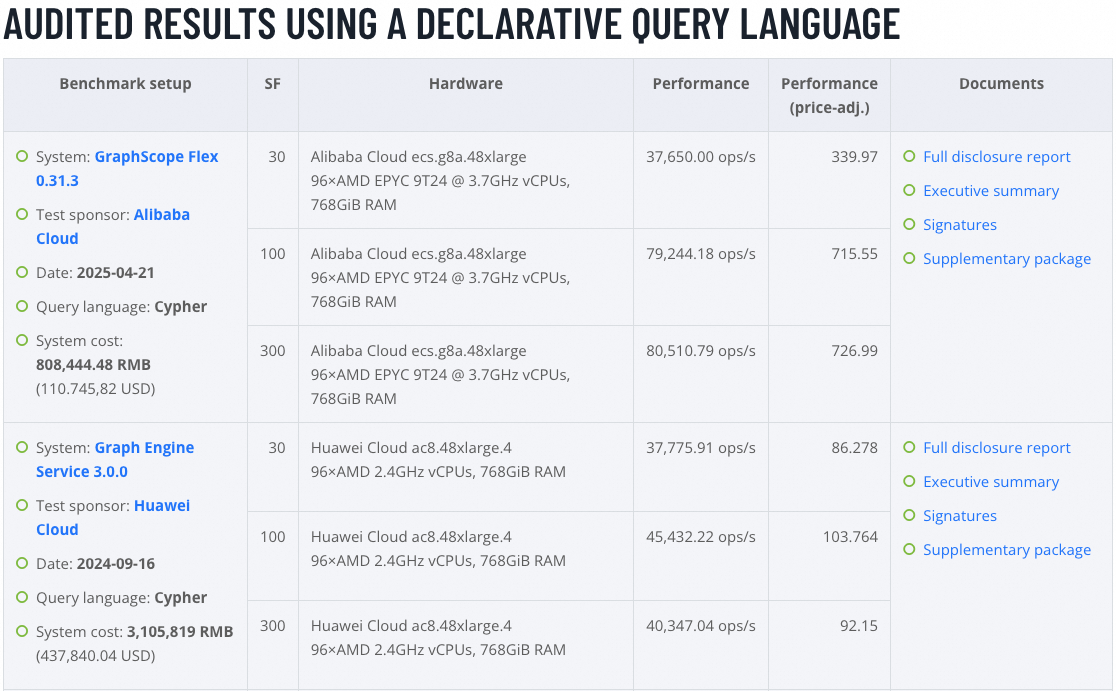
 The Linked Data Benchmark Council (LDBC) has released the latest results of its SNB Interactive Benchmark (via Declarative Queries), where GraphScope Flex achieved a historic breakthrough with a throughput exceeding 80,000 QPS (queries per second) – nearly twice the performance of the previous record holder!
The Linked Data Benchmark Council (LDBC) has released the latest results of its SNB Interactive Benchmark (via Declarative Queries), where GraphScope Flex achieved a historic breakthrough with a throughput exceeding 80,000 QPS (queries per second) – nearly twice the performance of the previous record holder!
LDBC is an internationally recognized authority in graph data and computing. Its Social Network Benchmark (SNB) simulates a Facebook-like social graph, covering CRUD operations, shortest-path queries, multi-hop traversals, and more, making it the industry’s gold standard for transactional online query performance evaluation. SNB supports two implementation approaches:
- Imperative: Requires graph experts to manually write and optimize queries in programming languages like C++.
- Declarative: Uses graph query languages like Cypher, with the system automatically optimizing execution.
In this benchmark, GraphScope Flex exclusively used declarative Cypher queries for all test cases, demonstrating not only its leadership in declarative query optimization and execution but also its full-stack technical prowess – from underlying storage to high-level optimization.
Full-Stack Optimization: Synergistic Advancements in Storage and Compute
GraphScope Flex’s record-breaking performance is built on innovations across storage, compute, and scheduling:
- Efficient Storage Structure: Employs a compact adjacency list format with vertex/edge compression and memory layout optimizations, enabling larger graph datasets on the same hardware.
- Intelligent Memory Management: Enhances traversal locality via prefetching and caching, significantly reducing memory access latency.
- High-Concurrency Transaction Support: Leverages MVCC (Multi-Version Concurrency Control) for high-throughput queries while maintaining low-latency data modification.
- End-to-End Vertical Optimization: Coordinated optimizations across storage, compute, and scheduling layers ensure peak performance.
A Milestone in Declarative Graph Query Optimization
Powered by its robust infrastructure, GraphScope Flex employs its in-house GOpt Optimization Framework to intelligently transform declarative queries into high-performance execution plans:
- Rule-Based Optimization (RBO): Pluggble heuristic rules (e.g., filter pushdown, field trimming, join fusion) optimize query plans, minimizing intermediate results and boosting efficiency.
- Automatic Type Inference: Dynamically deduces implicit type constraints in patterns, validating them against the data graph to avoid invalid traversals and improve cardinality estimation.
- Cost-Based Optimization (CBO): Uses high-order statistics and backend-registered cost models to search for optimal execution plans via branch-and-bound strategies, balancing data characteristics and system-specific implementations.
The research behind GOpt has been accepted by SIGMOD 2025. Additionally, we’ve published a detailed paper on arXiv outlining GraphScope’s optimizations for the LDBC SNB benchmark (paper link).
Leading in Both Declarative and Imperative SNB Leaderboard
GraphScope currently holds the performance record for imperative queries in the LDBC SNB Interactive benchmark. This latest breakthrough in declarative queries further cements its technical leadership – its declarative performance even surpasses other players’ records in imperative scenarios. This achievement proves that GraphScope Flex’s auto-optimized declarative queries are not only highly efficient and user-friendly, but also exceed manually tuned imperative solutions, dramatically lowering the barrier to high-performance graph querying.
Acknowledgments
The GraphScope team gratefully acknowledges the research contributions of Prof. Cheng Li (University of Science and Technology of China) and Prof. Ying Zhang (Zhejiang Gongshang University). Their rigorous prototype validation and performance benchmarking were instrumental in enhancingthe system’s performance during this benchmark evaluation.